Generate a Free Pricing Analysis, Understand Demand
Frequently asked questions
Our Amazon Price Elasticity Calculator looks at estimated sales data, historic product prices, and competitors to estimate the price elasticity for a specific product or product category.
Understanding your price elasticity is valuable for sellers who want to analyze the relationship between price and demand for their products on Amazon.
It provides insights into how customers will respond to price changes, whether an increase or decrease in price will lead to a significant change in demand, and how it will affect revenue and profitability.
By using an Amazon Price Elasticity Calculator, you can make data-driven decisions to find the optimal price point for your business objective. This data allows you to maximize revenue and profitability by considering both customer demand and competitive dynamics.
It can assist in making informed pricing decisions, optimizing product positioning, and improving overall sales performance on the platform.
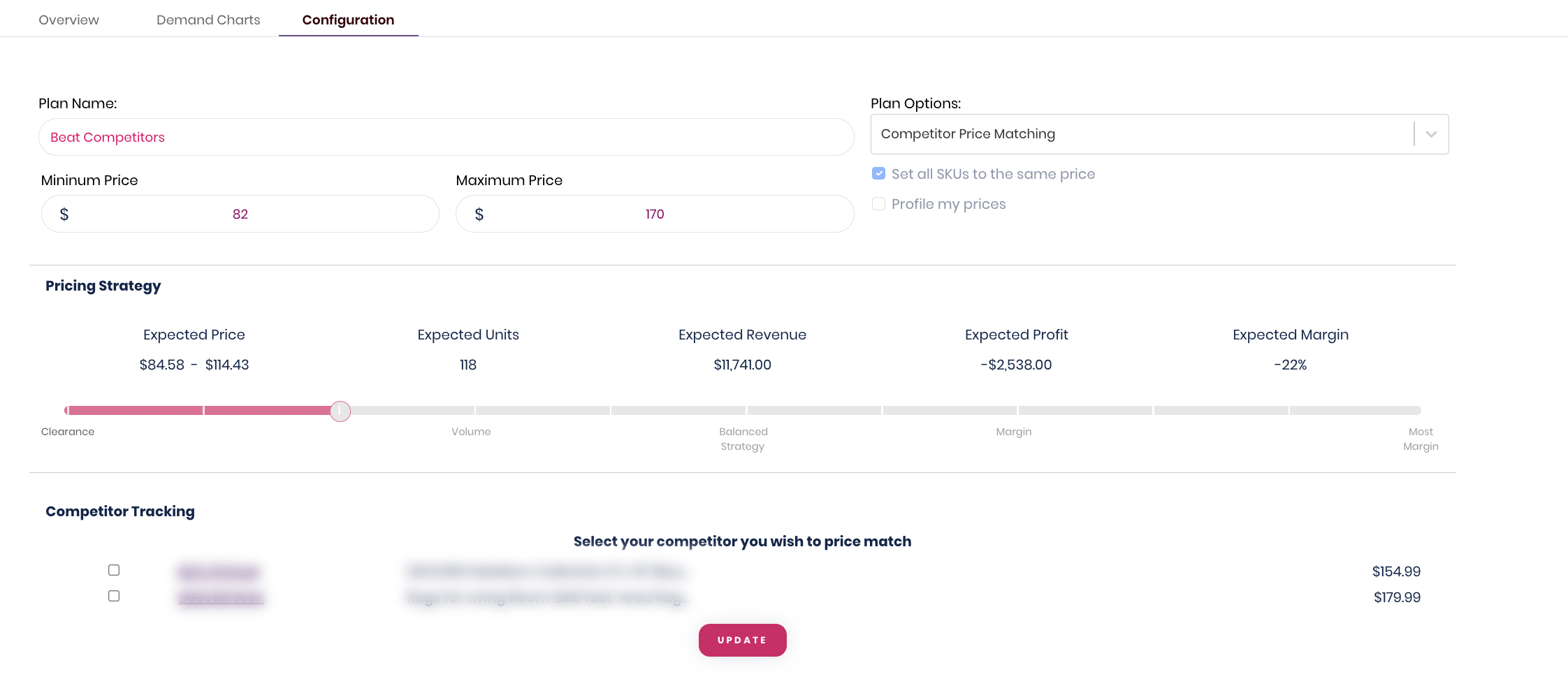
Deciding whether to change your price on Amazon and how often depends on various factors and requires careful consideration. Here are some points to help you make an informed decision:
- Competitive Landscape: Assess the pricing strategies of your competitors on Amazon. If you find that your prices are significantly higher than similar products from competitors, it may be worth considering a price adjustment to stay competitive. On the other hand, if you have a unique selling proposition or offer additional value, you might justify a higher price.
- Market Demand and Price Sensitivity: Evaluate the price sensitivity of your target customers and the overall demand for your product. If your product is price-sensitive and the market demand is elastic, lowering the price may attract more customers and potentially increase sales volume. Conversely, if your product is in high demand or has a relatively inelastic market, a price increase may not significantly impact demand and could help improve profitability.
- Profit Margins: Analyze your profit margins and consider how price changes might affect your overall profitability. Lowering prices to drive sales volume may result in lower margins, while raising prices could potentially improve margins but may impact sales volume. Strike a balance that ensures a healthy margin while remaining competitive.
- Seasonal Considerations: Take into account any seasonal fluctuations in demand for your product. Adjusting prices strategically during high-demand periods or special events can help capitalize on increased sales opportunities. Conversely, offering promotions or discounts during slower seasons might help maintain sales momentum.
- Customer Perception: Consider how price changes might impact customer perception of your product’s value. Abrupt or frequent price fluctuations may erode trust and credibility. Communicate any price adjustments transparently and effectively, emphasizing the value and benefits customers receive.
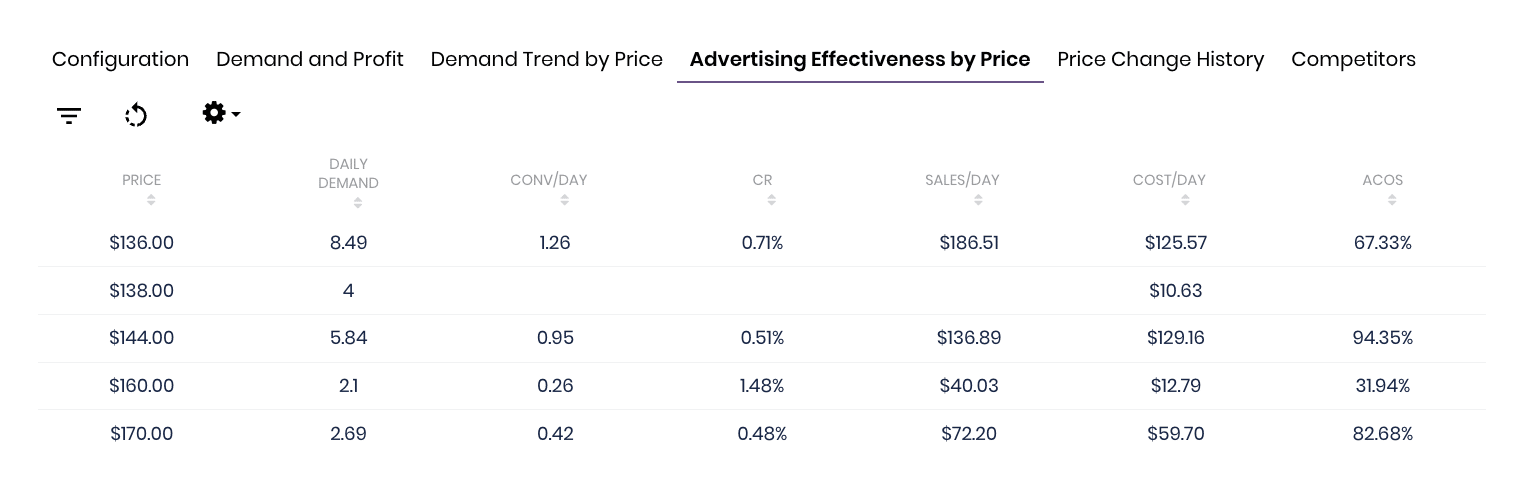
- Testing and Monitoring: If you are uncertain about the impact of price changes, consider conducting tests with different price points or utilizing Amazon’s dynamic pricing features. Monitor the results and gather data to assess the effects on sales volume, revenue, and profitability.
Ultimately, the decision to change your price on Amazon should be based on a comprehensive analysis of market conditions, competition, customer behavior, and your own business goals. It may be beneficial to gather data, consult pricing experts, and continuously monitor and evaluate the impact of price changes to ensure optimal results for your product and business.
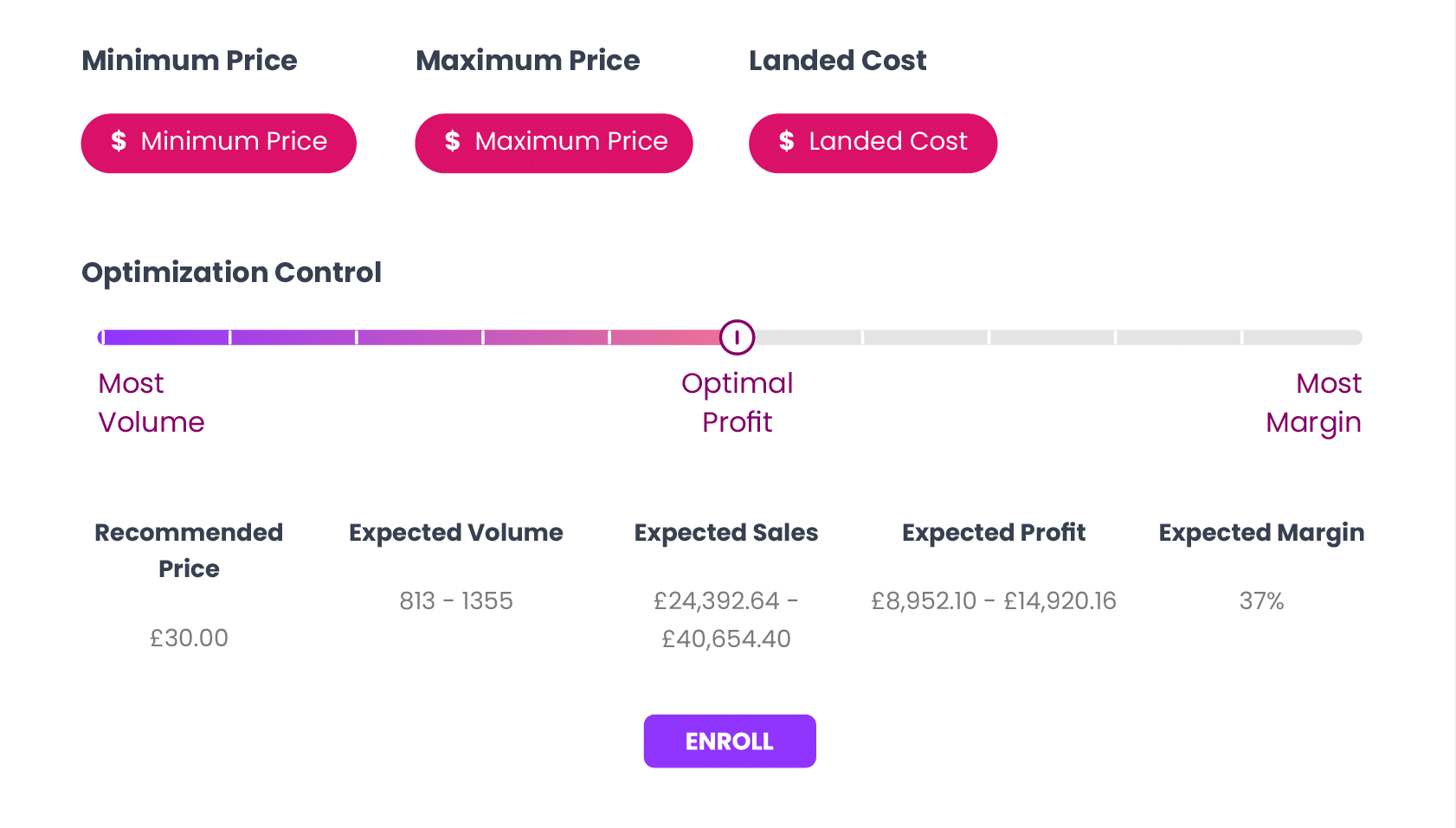
Using our Dynamic Pricing software put price changes on auto-pilot. We monitor the competition and demand for your products to ensure that they are priced to maximize profitability.
Learn more here: https://gotrellis.com/dynamic-pricing/
A pricing curve, also known as a demand curve, is a graphical representation that illustrates the relationship between the price of a product and the corresponding quantity of that product demanded by customers. It visually demonstrates how changes in price affect consumer demand.
In a typical pricing curve, the price of the product is represented on the vertical axis, while the quantity demanded is shown on the horizontal axis. The curve itself depicts the demand for the product at different price points. The shape of the curve can vary depending on the price elasticity of the product.
A downward-sloping pricing curve indicates that as the price decreases, the quantity demanded increases. This suggests an elastic demand, where customers are sensitive to price changes and a lower price stimulates higher demand. In this scenario, a small decrease in price can result in a significant increase in the quantity of products sold.
Conversely, an upward-sloping pricing curve suggests an inelastic demand, where customers are less responsive to price changes. The quantity demanded remains relatively stable even as the price increases. In this case, changes in price have a minimal impact on consumer demand.
The shape and slope of the pricing curve can provide valuable insights for pricing strategies. By understanding the elasticity of demand for a product, businesses can determine the optimal price point that maximizes revenue and profitability. It helps identify the price range where demand is most responsive, enabling businesses to make informed pricing decisions to attract customers and achieve their desired sales objectives.
An elastic price refers to a situation where changes in price have a significant impact on the quantity demanded or purchased by customers. In other words, when the price of a product changes, customers are highly responsive to that change, and even small fluctuations in price can lead to a notable change in demand. If a product has an elastic price, a price increase may result in a decrease in sales volume, while a price decrease may lead to an increase in sales.
On the other hand, an inelastic price describes a situation where changes in price have a minimal effect on the quantity demanded. In this case, customers are less responsive to price changes, and variations in price have a relatively small impact on demand. If a product has an inelastic price, a price increase may not significantly reduce sales volume, while a price decrease may not substantially increase sales.
The price elasticity of a product is influenced by several factors, including the availability of substitutes, consumer preferences, brand loyalty, and the proportion of income spent on the product. Products that have many substitutes and are considered non-essential or luxury items tend to have more elastic prices. Conversely, products that are necessities or have limited substitutes tend to have more inelastic prices.
Understanding the elasticity of a product’s price is important for businesses to make pricing decisions and assess the potential impact on demand and revenue. It helps determine the optimal pricing strategy, considering factors such as market competition, consumer behavior, and the overall price sensitivity of the product.
The price elasticity of demand is simply calculated by measuring how much sales change when you change your price.
This can be calculated by the formulate below:
Price of Elasticity of Demand =
[(Sales Change – Initial Sales)/(Sales Change + Initial Sales)] /
[(Price Change – Initial Price)/(Price Change + Initial Price)]
Put simply,
Price Elasticity of Demand =
Sales Change/Price Change
Trending Posts
Amazon Inventory Management: Ultimate Guide For Sellers
How To Create An Automated Amazon Business
Dynamic Pricing To Match Demand, Everyday
Our customers sleep well knowing that their products are priced to match the market. Schedule a demo to see how you can too.
Schedule a Demo